A decade in the past, Korea’s enterprise ecosystem appeared like a well-recognized story: male founders, male-heavy groups, and a pipeline constructed round manufacturing-era assumptions. The newest official survey knowledge counsel that mannequin is slowly loosening. Ladies are nonetheless a minority amongst founders, but their share has practically doubled in ten years. The extra revealing sign sits inside hiring and job construction, the place the enterprise sector’s shift towards software program and IT companies is reshaping who enters, who stays, and who will get secure roles.
Korea Enterprise Survey 2024: Feminine Founders Rise to 9.7%
Korea’s Enterprise Enterprise Detailed Standing Survey reveals a transparent change in founder gender composition over the previous decade. In 2014, venture-company founders had been 94.7% male and 5.3% feminine. By 2024, the break up moved to 90.3% male and 9.7% feminine.
Employment construction shifted alongside founder composition. Male employment in enterprise corporations rose from 525,484 in 2014 to 579,899 in 2024, a ten.4% improve. Feminine employment grew quicker, rising from 191,541 to 248,478, up 29.7%.
That pushed girls’s share of the enterprise workforce from 26.7% to 30.0% over ten years.
An business official tied the development to industrial change contained in the enterprise sector, saying:
“Because the enterprise ecosystem has shifted from a manufacturing-centered base to software program and data expertise–primarily based companies, job features have diversified, and the influx of feminine expertise has elevated.”
IT Providers Shift Reshapes Korea Startup Expertise Pipeline
This founder ratio issues, but the employment numbers clarify extra about how the ecosystem is evolving. Hiring is the place industrial construction turns into lived actuality.
The survey suggests girls are getting into the enterprise labor market quicker than males because the sector’s heart of gravity strikes towards software program and IT-based companies. That shift tends to develop function variety, particularly in features that scale by product iteration, service design, knowledge operations, buyer success, and enterprise supply.
The founder pipeline nonetheless skews closely male at 90.3%. But the workforce sign appears totally different. A 30.0% feminine share inside enterprise corporations isn’t parity, but it surely signifies that expertise composition is altering on the working stage even earlier than it totally modifications on the possession stage.
Common vs Non-Common Jobs Reveal Labor Stress in Startups
Probably the most uncomfortable pressure within the knowledge isn’t founder share. It’s job high quality and the place danger sits.
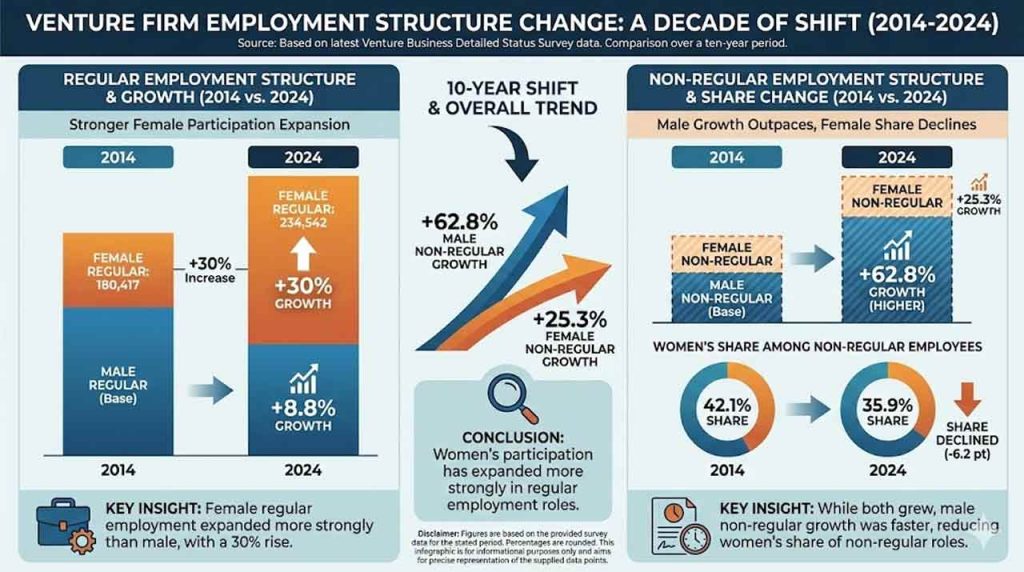
Common employment grew for each genders, but the tempo diverged. Male common workers rose from 510,208 in 2014 to 550,525 in 2024, up 8.8%. Feminine common workers elevated from 180,417 to 234,542, up 30% over the identical interval.
Non-regular employment moved in a unique course. Male non-regular employment rose by 62.8% over ten years, whereas feminine non-regular employment elevated by 25.3%. Ladies’s share amongst non-regular employees fell from 42.1% in 2014 to 35.9% in 2024.
That blend complicates the simple narrative. Ladies gained extra floor in common roles, but the enterprise sector nonetheless expanded non-regular work sharply amongst males. The image that emerges is a labor market below stress to remain versatile because it transitions towards service-heavy progress, even whereas it professionalizes elements of the workforce.
What the Information Reveals About Gender Progress — and Its Limits
These survey outcomes allow a grounded conclusion: girls’s participation in Korea’s enterprise ecosystem is rising in founders and employment, and the shift correlates with the sector’s transfer towards software program and IT companies.
The info doesn’t show causality. It additionally doesn’t reveal which industries inside enterprise corporations are driving the founder change, nor does it present how capital allocation behaves. Ladies entrepreneurship’s share rising to 9.7% is significant, but it nonetheless leaves girls as a small fraction of those that management technique, fairness, and board affect.
The numbers additionally don’t seize the lived boundaries that form who turns into a repeat founder, who raises institutional rounds, and who exits. These outcomes require separate knowledge.
Nonetheless, the last decade development is difficult to dismiss. It indicators a enterprise ecosystem that’s slowly rewriting its inside demographics alongside its industrial base.
Why Korea’s Enterprise Gender Shift Issues to International Buyers
Korea is usually mentioned as a capital-efficient, hardware-capable, export-driven innovation market. The survey highlights one other function international stakeholders ought to worth in: the enterprise ecosystem’s labor base is evolving as software program and IT companies develop.
Worldwide founders evaluating Korea ought to learn this as a expertise sign. A bigger feminine share in enterprise employment can broaden management pipelines, particularly in product-led and service-led ventures that depend on cross-functional execution.
Buyers additionally ought to deal with the 9.7% founder share as an early indicator, not a end line. Deal stream composition not often shifts in a single day. It shifts when expertise inflows, secure roles, and repeatable operational careers create extra founders who can credibly increase capital.
On the identical time, policymakers ought to see the structural lever within the knowledge. Industrial composition does matter. When enterprise exercise strikes towards software program and IT companies, workforce variety can change even and not using a single headline coverage intervention.
A Structural Workforce Shift Inside Korea’s Startup Financial system
The tempting story is celebration. The extra helpful story is prognosis.
Ladies’s founder share rising from 5.3% to 9.7% displays progress, but it surely additionally underlines how far the ecosystem nonetheless has to go. The deeper sign is that Korea’s enterprise corporations are hiring otherwise because the sector shifts away from manufacturing-centered fashions and towards software program and IT companies.
That change is much less seen than a fund launch or a coverage speech. It is usually extra sturdy, as a result of it alters who will get expertise inside high-growth corporations. Over time, that have turns into the uncooked materials of latest founders.
Key Takeaway on Korea’s Feminine Founders 2024
- Korea’s Enterprise Enterprise Detailed Standing Survey reveals feminine founders rose from 5.3% in 2014 to 9.7% in 2024, whereas male founders fell from 94.7% to 90.3%.
- Ladies’s share of venture-firm employment elevated from 26.7% to 30.0% over the last decade.
- Feminine employment in enterprise corporations grew 29.7% over ten years, in contrast with 10.4% progress for males.
- Feminine common employment rose 30% over the last decade, outpacing 8.8% progress for male common employment.
- Ladies’s share amongst non-regular employees declined from 42.1% in 2014 to 35.9% in 2024, whereas male non-regular employment rose sharply.
- An business official linked the development to a shift within the enterprise ecosystem away from manufacturing and towards software program and IT service fashions, which diversified roles and elevated inflows of feminine expertise.
– Keep Forward in Korea’s Startup Scene –
Get real-time insights, funding updates, and coverage shifts shaping Korea’s innovation ecosystem.
➡️ Comply with KoreaTechDesk on LinkedIn, X (Twitter), Threads, Bluesky, Telegram, Fb, and WhatsApp Channel.
Elevate your perspective with NextTech Information, the place innovation meets perception.
Uncover the most recent breakthroughs, get unique updates, and join with a worldwide community of future-focused thinkers.
Unlock tomorrow’s tendencies right now: learn extra, subscribe to our e-newsletter, and develop into a part of the NextTech neighborhood at NextTech-news.com

