Query:
MoE fashions include way more parameters than Transformers, but they will run quicker at inference. How is that potential?
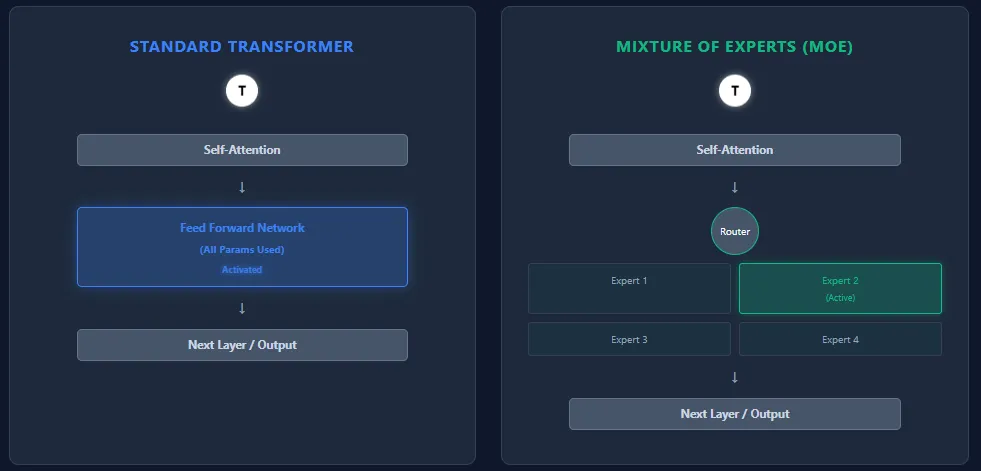
Distinction between Transformers & Combination of Specialists (MoE)
Transformers and Combination of Specialists (MoE) fashions share the identical spine structure—self-attention layers adopted by feed-forward layers—however they differ basically in how they use parameters and compute.
Feed-Ahead Community vs Specialists
- Transformer: Every block accommodates a single massive feed-forward community (FFN). Each token passes via this FFN, activating all parameters throughout inference.
- MoE: Replaces the FFN with a number of smaller feed-forward networks, referred to as specialists. A routing community selects only some specialists (High-Ok) per token, so solely a small fraction of complete parameters is energetic.
Parameter Utilization
- Transformer: All parameters throughout all layers are used for each token → dense compute.
- MoE: Has extra complete parameters, however prompts solely a small portion per token → sparse compute. Instance: Mixtral 8×7B has 46.7B complete parameters, however makes use of solely ~13B per token.
Inference Value
- Transformer: Excessive inference price as a consequence of full parameter activation. Scaling to fashions like GPT-4 or Llama 2 70B requires highly effective {hardware}.
- MoE: Decrease inference price as a result of solely Ok specialists per layer are energetic. This makes MoE fashions quicker and cheaper to run, particularly at massive scales.
Token Routing
- Transformer: No routing. Each token follows the very same path via all layers.
- MoE: A realized router assigns tokens to specialists based mostly on softmax scores. Totally different tokens choose completely different specialists. Totally different layers might activate completely different specialists which will increase specialization and mannequin capability.
Mannequin Capability
- Transformer: To scale capability, the one possibility is including extra layers or widening the FFN—each improve FLOPs closely.
- MoE: Can scale complete parameters massively with out growing per-token compute. This permits “larger brains at decrease runtime price.”
Whereas MoE architectures supply huge capability with decrease inference price, they introduce a number of coaching challenges. The most typical situation is knowledgeable collapse, the place the router repeatedly selects the identical specialists, leaving others under-trained.
Load imbalance is one other problem—some specialists might obtain way more tokens than others, resulting in uneven studying. To deal with this, MoE fashions depend on strategies like noise injection in routing, High-Ok masking, and knowledgeable capability limits.
These mechanisms guarantee all specialists keep energetic and balanced, however in addition they make MoE programs extra advanced to coach in comparison with commonplace Transformers.



I’m a Civil Engineering Graduate (2022) from Jamia Millia Islamia, New Delhi, and I’ve a eager curiosity in Information Science, particularly Neural Networks and their software in numerous areas.
Elevate your perspective with NextTech Information, the place innovation meets perception.
Uncover the most recent breakthroughs, get unique updates, and join with a world community of future-focused thinkers.
Unlock tomorrow’s tendencies at this time: learn extra, subscribe to our e-newsletter, and turn into a part of the NextTech neighborhood at NextTech-news.com

